Explore how Amazon’s expanding robot workforce boosts efficiency and safety in warehouse operations. Discover the impact of robots like Sequoia and Digit on logistics and employment.
Table of Contents
Amazon
Amazon continues to cement its position as a pioneer in the automation of warehouse operations with a rapidly growing fleet of robots.
Over the last three years, the number of robots in its warehouses has more than doubled, marking a significant shift in how the company manages its vast logistics operations.
Surge in Robot Numbers
From a substantial 350,000 units in 2021 to an awe-inspiring 750,000 by mid-2023, Amazon’s deployment of robots in its fulfillment centers and warehouses has seen a staggering increase.
This escalation underscores the company’s commitment to enhancing efficiency and solidifies Amazon’s position as the world’s largest manufacturer of industrial robots, a testament to its technological prowess and forward-thinking approach.
Growth of Amazon’s Robot Fleet
| Year | Number of Robots |
|---|---|
| 2021 | 350,000 |
| 2023 | 750,000 |
Innovations in Robotics
Amazon’s arsenal includes various robots, each with specialized functions designed to streamline operations and reduce the physical strain on employees.
Among the notable robots are Robin and Sparrow, which are instrumental in sorting customer orders.
These were developed at Amazon’s Robotics Innovation Hub near Boston.
Robots at a Glance
- Proteus and Hercules: These robots, which resemble the household vacuum Roomba, are tasked with moving items like containers around warehouses.
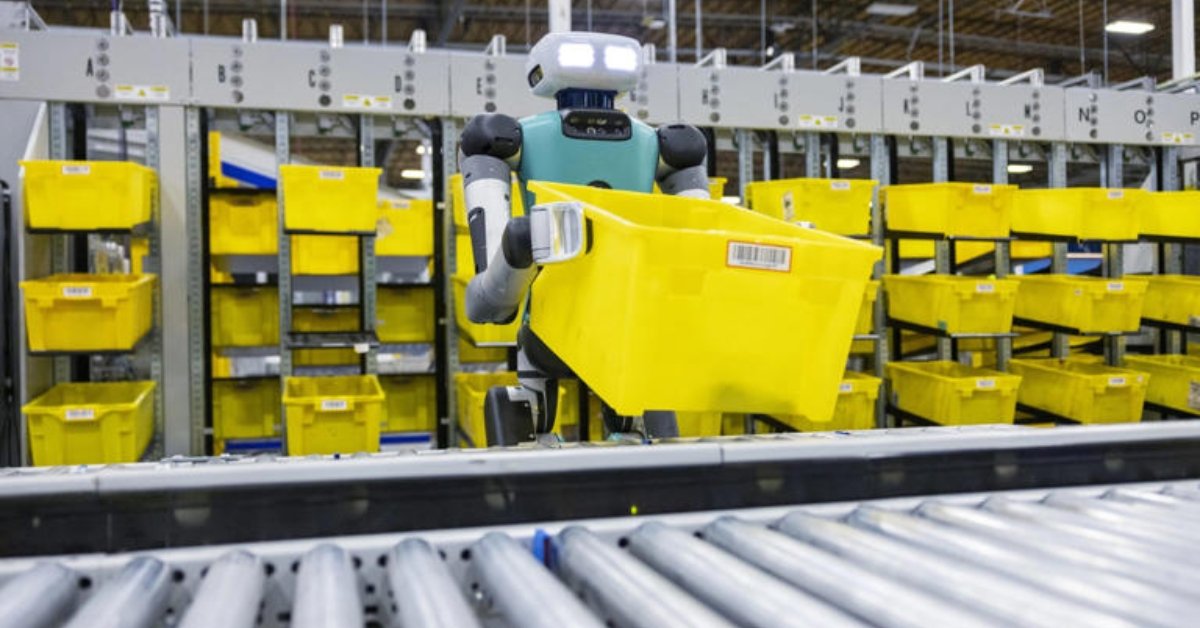
- Sequoia: This robotic system lifts and sorts containers, significantly reducing the need for employees to perform strenuous bending and stretching motions.
Furthermore, Amazon has begun testing a humanoid robot named Digit, developed by Agility Robotics, to assist in warehouse tasks, indicating a forward-thinking approach to future automation possibilities.
Enhanced Efficiency and Safety
The introduction of these robotic systems has not only sped up operations but also improved safety conditions.
The Sequoia system, for instance, has increased the speed of inventory management by 75% and reduced the order processing time by as much as 25%.
In 2022, Amazon reported a 15% reduction in recorded incident rates and an 18% decrease in lost-time incident rates at sites equipped with robotics compared to those without.
Robots Complementing the Human Workforce
Despite the rapid increase in robotic workers, Amazon’s human workforce remains substantial, with over 1.525 million employees at the end of the last year.
The integration of robots has not led to a decrease in human jobs but rather an evolution of the workforce.
According to Stefano La Rovere, director of global robotics at Amazon, the introduction of robots and technology has reduced the walking distance between assignments, alleviated repetitive motions, and aided in lifting heavy weights, thus enhancing overall employee productivity.
Moreover, over 700 new job categories have been created due to technological integration within the company, dispelling concerns that robots would replace human workers.
Looking Forward
As Amazon continues to expand its robotic workforce, the synergy between human employees and robotic technology is poised to set new standards in operational efficiency and worker safety in the logistics industry.
This strategic enhancement underscores Amazon’s bullish outlook on the future of robotics in improving warehouse operations.